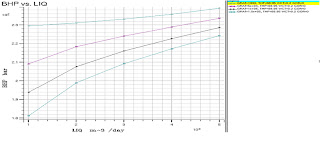
•A gas-lift system provides production energy by injecting gas into the production fluid column, thereby reducing the hydrostatic pressure and enabling improved reservoir production.
Purposes of Gas Lift optimization
What is the optimum amount of lift gas required for a well to achieve its production target?
•optimizing gas lift within a group of wells
How should a limited supply of lift gas be best distributed among the individual wells in order to achieve its group production target?
•optimizing gas lift within a simple network
For sub-sea manifold group of wells, how do the pressure losses in a flow line affect the optimum distribution of lift gas to the wells?
Gas Lift without optimization
•VFPPROD -record 1, item 7 - definition of ALQ: GRAT, IGLR, TGLR
•WCONPROD - item 12
•WELTARG - item 2 -LIFT
•WLIFT - item 5 - new ALQ; item 10 incremental of ALQ
Optimizing Individual Wells
•Divide the lift gas supply into discrete increments of uniform size
•Examine effect of increasing lift gas to each well by one increment. Calculate the well’s weighted incremental gradient (WIG)
•Examine effect of reducing lift gas to each well by one increment. Calculate the well’s weighted decremental gradient (WDG)
Add lift gas to the well as long as its weighted incremental gradient > the minimum economic gradient (MEG) Optimizing Groups
•Update the distribution of the lift gas increments currently allocated to the group:
•move an increment from well w2 to w1 if maxWIG(w1)>minWDG(w2)
•until there is no exchange
•Remove from the group any surplus increments
•>production rate limit
•>lift gas supply limit
•well’s WDG<MEG
•Add lift gas increment to the well
•with largest WIG>MEG
•<its own lift gas supply limit
•<its group’s lift gas supply limit
Optimizing Gas Lift in a Network
•Whenever a lift gas increment is added or subtracted, WIG & WDG must be
recalculated for all the wells in the field
•reason: change in Q affects THPs of other wells in the network
•Each time WIG & WDG are recalculated, the whole network must be rebalanced
•computation time proportional to square of the no. of wells multiplied by no. of lift gas increments added/subtracted
•recommend to use NETBALAN to decrease the network convergence tolerance
by a factor of 10.