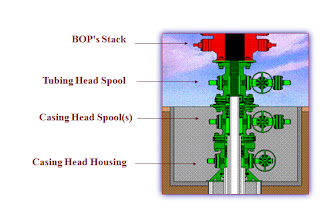
Tubinghead and X-mas tree
Tubinghead
•Surface equipment from which the tubing is
suspended
Xmas tree or valve array
•Used to control well during production
•Mounted above wellhead
•Typically sourced from same manufacturer
Primary functions of tubinghead
•Suspend tubing with hanger
•Seal between tubing and annulus
•Provide access ports to annulus
–gaslift gas
–inhibitor injection
–circulating the well
•Provide mounting for adapter flange or Xmas tree
Tubing Hanger Types
•Threaded Hanger Flange
–used in low pressure wells (e.g. Pumping wells)
•Boll Weevil Type
•Ram Type Tubing Hanger
•Boll Weevil Type
Tubing Hanger for Bowl Type Tubing Head.
Boll-Weevil type hanger and housing
Spool and Hanger
Hangers for Dual Completion
•Ram Type Tubing Hanger
–allows free tubing manipulation to latch tubing in
tension
Tubing tension hanger Cameron SRT
Tubing Hanger with Extended Neck
Hanger may have extended neck
•Projects into base of X-mas tree or adapter
flange
•Sealed flow path through wellhead
Xmas tree or adapter interface