High Strength
Tubing Failure
Tubing Failure
Failures of high-strength tubing are normally caused by:
- Manufacturing defects
- Handling/transportation damage
- Hydrogen embrittlement
API Tubing
Connections
Connections
There are two standard API coupling tubing connections available:
The API EUE type of connection is available in 23/8”, 27/8”, 31/2” and 41/2”.
Extra Clearance
It is occasionally necessary to provide extra clearance to enable tubing
installation. To accommodate this, API couplings can be turned down (to
specified tolerances) without loss of joint strength. Special clearance collars
are usually marked with a black ring in the center of the color band indicating
steel grade. Extra-clearance, coupling-type thread forms have been developed
for non-upset tubing which have 100% joint strength.
Integral-joint premium threads provide additional clearance and are available
in a number of configurations. Some can be turned down to provide even
greater clearance. This type of joint is more expensive and is generally used in
special situations (high-pressure or gas well application).
Premium Tubing
Connections
Connections
In addition to the standard API connections, there are a wide variety of specific
joint connections available usually referred to as premium connection. Most
premium connections use a metal-to-metal seal which requires that the mating
pin and box surfaces are forced together with sufficient stress to establish a
bearing pressure greater than the differential pressure across the connection.
The bearing pressure (Pb) is defined as the pressure exerted between the metal
surfaces created by the torque used at make-up.
Premium connections are available in a wide variety of types, weights and
materials
Connection Seals
Round thread connections form several metal-to-metal seals between the tapered
portions of pin and box surfaces. The small void between the crest and root of
the mating threads must be filled with thread compound solids in order to
transmit adequate bearing pressure from one threaded surface to another.
Some connections (e.g., HYDRIL) have large smooth metal-to-metal
connections. The threads in this type of connection have a relatively large
clearance and do not act as seals. Threads like Armco Seal Lock have both a
sealing thread and a smooth metal scaling surface (Fig. 10). A Teflon ring is
used in some premium connections to provide a supplementary seal and provide
corrosion protection.
The stresses applied during make-up and subsequent service determine the
success of the connection seal. When compiling tubular make-up procedures
the minimum, optimum and maximum torque for each connection type must be
known.
Basic String Design
and Selection
and Selection
When selecting completion components, consider the factors shown below.
This of course is in addition to the basic efficiency, safety and economic
requirements of all completions.
- Facilitate installation
- Optimize production
- Simplify maintenance
- Enable stimulation or workover
- Provide for contingency
Tubular
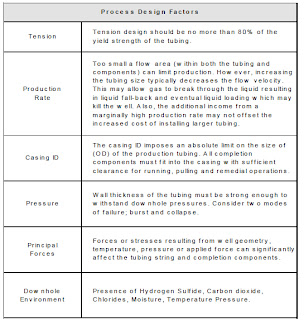
Design Factors
Design Factors
The basic string design and selection process should take into
account the following guidelines before detailed planning is begun:
Drift Inspection
Before running in the hole, drift the tubing with an API drift mandrel to ensure
the internal clearance is within tolerance.
Handle all tubing (new, used or reconditioned) with thread protectors in place.
Do not remove the thread protectors until the tubing is ready to be stabbed.
High-strength tubing is particularly susceptible to damage caused by improper
shipping and handling practices.
Measurement
When running tubing and completion components, careful measurement of
each joint or item is essential. Each measurement is recorded in a tally book
against the joint number which should be clearly marked on each joint. The
tape used is divided into feet and decimal fractions, (e.g., the reading for 20 ft.,
6 in., would be read as 20.5 ft.).
Tubing joints (and other string components) are measured from the box end to
the beginning of the threads on the pin end (not the end). Record completion
components on a separate sheet of the tally book. The length, OD, grade and
ID are listed as appropriate for each component.
When the grade and size of pipe has been chosen, details of the following
points should be made known to field personnel:
- Handling - Tubing, especially high grade tubing (P-105, etc.)
- Torque - Too loose or too tight make-up on a joint connection
- Record (Tally) keeping - Accurate measuring and recording of
packer accidentally placed below the perforated interval is a prime
example of mis-measuring or miscounting tubing joints.
Running the
Tubing String
Tubing String
NOTE: Use PPE equipment.