SECTION A
KEY DEFINITIONS
Drilling Ahead
WHAT IS A KICK?
IT IS AN INFLUX OF FORMATION FLUID
THAT CAUSES THE WELL TO FLOW.
WHAT IS A BLOWOUT?
AN UNCONTROLLED EXIT OF THE FORMATION FLUIDS
AT THE SURFACE
Hydrostatic Pressure
Hydro- means a fluid
Static- means at rest
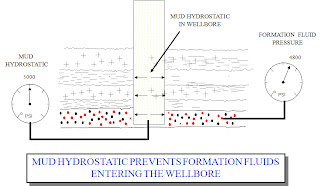
Hydrostatic in the wellbore is from the mud
MUD HYDROSTATIC
VERTECAL WELL
STANDERED FORMULA WITH FT., PPG AND PSI
MUD HYDROSTATIC HP = 0.052 X MUD WEIGHT X DEPTH
MUD GRADIANT = 0.052 X MUD WEIGHT PSI\FT.
Pressure (psi) = Mud Weight x .052 x TVD
Pressure Gradient (psi/ft) = Mud Weight, ppg x .052
Pressure Gradient (psi/ft) =Pressure, psi ¸ TVD, ft
Mud Weight, ppg = Pressure Gradient ¸ .052
Mud Weight (ppg) = Pressure ¸ TVD ¸ .052
TVD (ft) = Pressure (psi) ¸ Mud Weight (ppg) ¸ 0.052
Fluid present in the pore space of the rock.
FORMATION PRESSURE
The pressure of the formation fluids.
What is formation fluid pressure?
Formation Pressure: is the fluid pressure in the pore spaces of the formation.
BOTTOM HOLE PRESSURE
IT IS THE TOTAL PRESSURES EXERTED AT THE BOTTOM OF THE WELL.
Balance
Mud Hydrostatic =Formation Pressure
Overbalance
Mud Hydrostatic > Formation Pressure
Underbalance
Mud Hydrostatic < Formation Pressure
1-PREVENTING A KICK
PRIMARY
2-SHUTTING IN THE WELL AFTER A KICK HAS BEEN TAKEN SECONDARY
Primary control
Secondary ControlBlowout Preventers
Mud Hydrostatic and Formation Pressure
Always Remember that HP and FP are two opposite forces.